Botulinum toxin is a powerful poison that is made by a bacterium, called clostridium botulinum. The effect of the toxin is to weaken or paralyze muscle by interfering with the message that the nerve gives to the muscle to contract.
Outbreaks of botulism have occurred associated with the consumption of improperly preserved foods. The problem arises when the food is canned or jarred such that the bacteria grow and produce the toxin. When the improperly preserved food is eaten, the toxin is absorbed into the bloodstream and causes weakness of the muscles, including the muscles for breathing. The weakness is temporary.
The botulinum toxin used in clinical practice is purified so there are no bacteria or other contaminants. The doses recommended to treat spasmodic torticollis are well below doses that could cause human botulism. Overall, botulinum toxin has been found to be a safe and effective treatment for a variety of disorders, including spasmodic torticollis.
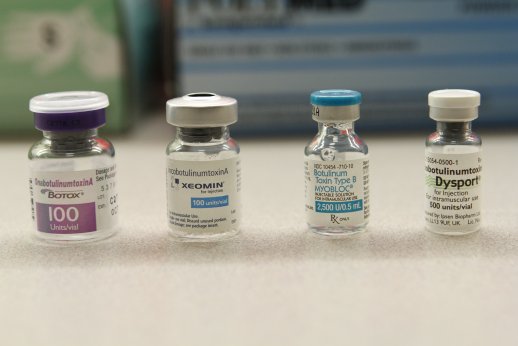
There are currently four brands of botulinum toxins approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of spasmodic torticollis in the United Stated.
| Product Name | Botulinum Toxin Type | Manufacturing Company | Website |
| Botox® | Type A | Allergan | www.botoxmedical.com |
| Daxxify® | Type A | Revance | www.daxxifytherapy.com |
| Dysport® | Type A | Ipsen | www.dysport.com |
| MyoBloc® | Type B | Solstice Neuroscience | www.myobloc.com |
| Xeomin® | Type A | Merz Pharmaceuticals | www.xeomin.com |
If you are interested in learning more about botulinum toxin, contact the NSTA at NSTAmail@aol.com

